India - Energy Market
India’s announcement that it aims to reach net zero emissions by 2070 and to meet 50% of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030 with numerous policy measures paves the way for growth of renewable electricity sector in India at a faster rate than any other major economy.
India’s Energy Sector Overview
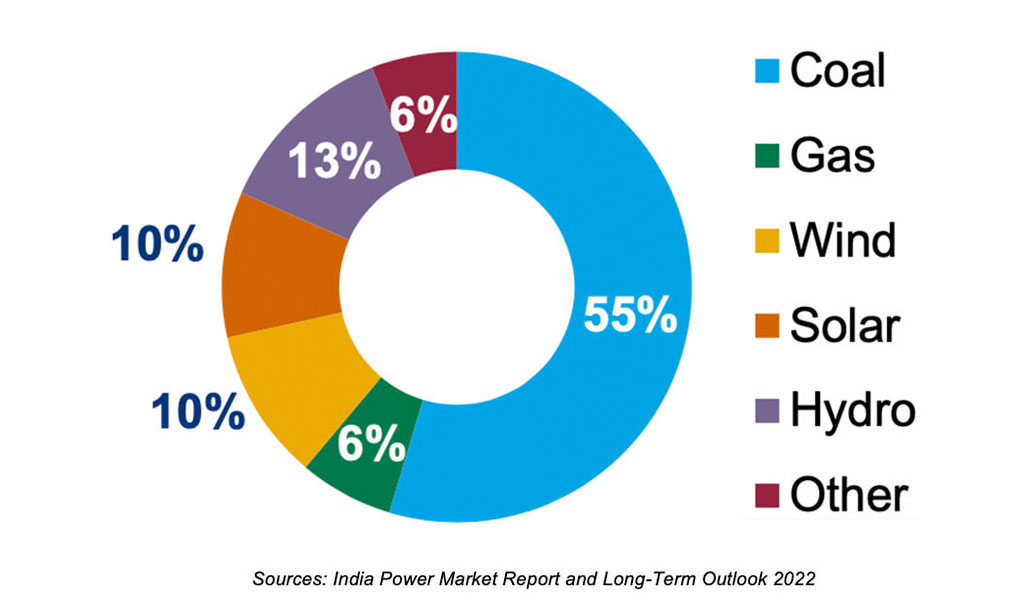
Installed Power Capacity (2021)
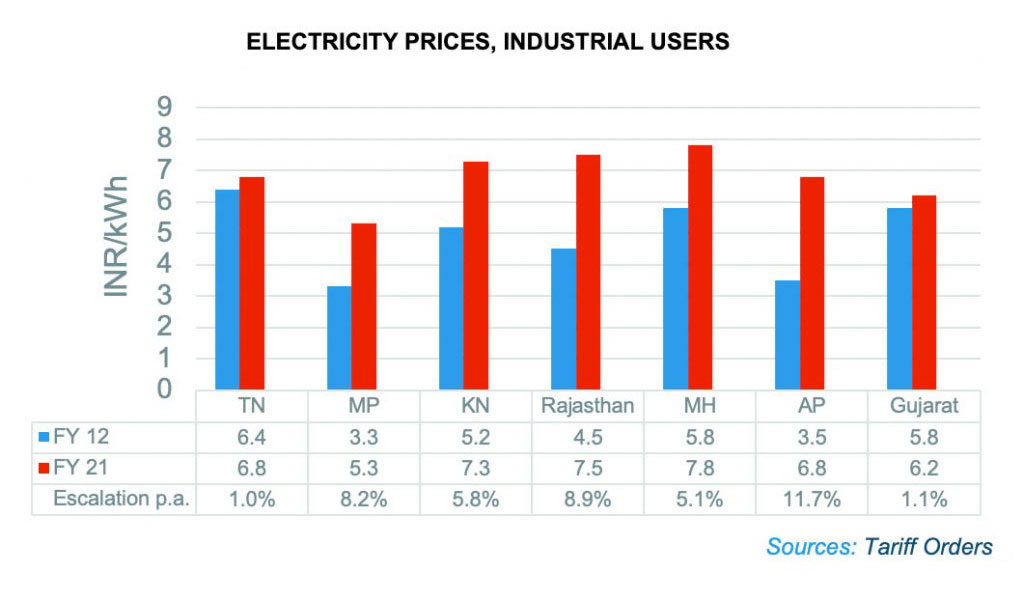
Average Electricity Prices, (Industrial User)
- As per World Energy Outlook 2021 of IEA, the current share of India in global primary energy consumption is 6.1% and is likely to increase to about 9.8% under stated policies scenario by 2050
- Owing to technological developments, steady policy support and a vibrant private sector solar power plants are cheaper source of electricity
- Commercial & Industrial customers pay high power tariffs because they subsidize the low power tariffs of the residential and agricultural sectors
Regulation
Government Lead Initiatives:
- In November 2021, at the Cop-26 Summit in Glasgow, India set ambitious targets to produce 50% of its electricity from renewable sources and install 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Ministry of Power (MoP), Government of India (GoI) notified the Electricity (Promoting Renewable Energy Through Green Energy Open Access) Rules, 2022 to promote the Green Energy open access across India. This will reduce the diversification of practices related to open access in the states.
- Waivers of open access charges and banking facility offered by multiple state electricity regulators gives incentive to Commercial and Industrial customers to move to Solar Energy.
Implementation:
- In the Union Budget 2022-23, the allocation for the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI), which is currently responsible for the development of the entire renewable energy sector, stood at Rs. 1,000 crores (~US$ 132 million).
- Investment in renewable energy in India reached a record US$ 14.5 billion in FY22, an increase of 125% over FY21.
