Japan - Energy Market
Japan has one of the most liberalized power markets in the Asia Pacific and has implemented multiple revenue streams to promote renewables
Japan’s Energy Sector Overview
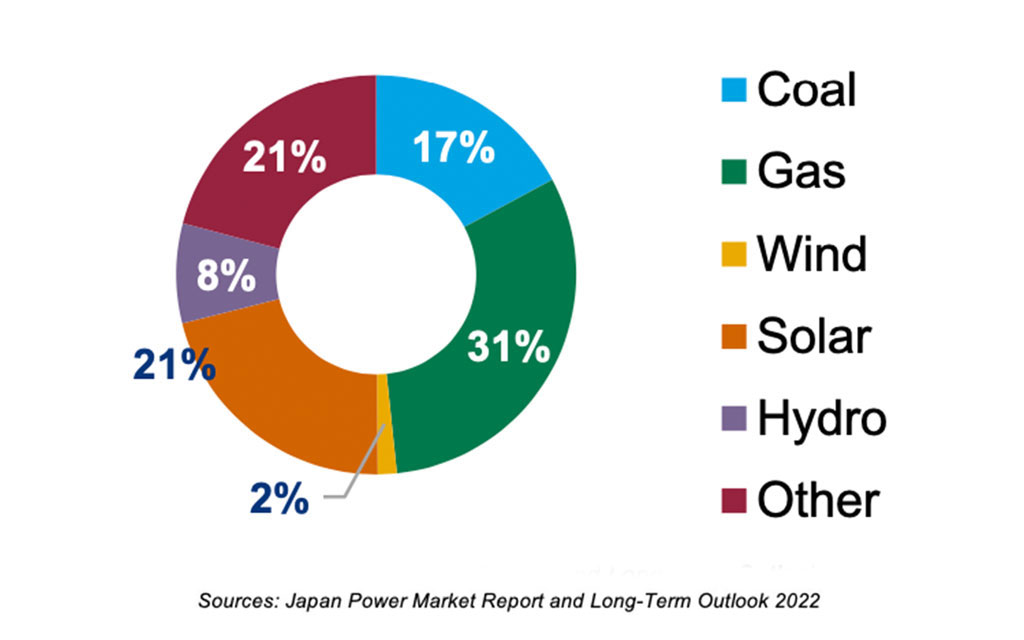
Installed Power Capacity (2021)
- Renewable Energy Sources targets: 36% to 38% renewables share target by 2030 – PV capacity should hit 104 to 118 GW, set by METI in 2021
- Under the Strategic Energy Mix Plan of Japan, 14% to 16% of the primary energy is expected from PV by 2030
- Carbon reduction target: reduce GHG emissions by 46% by 2030 compared with 2013, including 53% in the power sector
Average Electricity Prices (C&I MV Users)
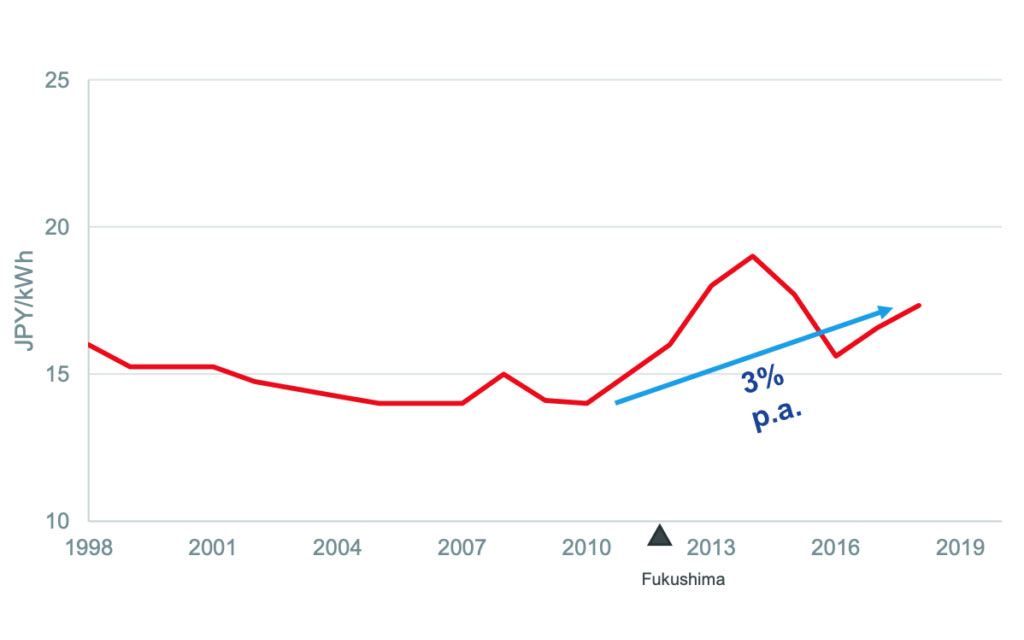
- Average electricity price (C&I MV users) currently goes over ¥15/kWh price since Ukraine Crisis in 2022
- Grid electricity users shall bear additional cost for RE surcharge, which is ¥3.45/kWh @FY2022. RE surcharge is increasing at CAGR34%
- C&I solar LCOE (levelized cost of electricity) goes below average electricity price plus the RE surcharge (grid parity) in Japan
Regulation
Government Lead Initiatives:
- Japanese government adopted 6th Strategic Energy Plan aiming at carbon neutrality by the end of 2050 while enhancing energy security. The plan also presents roadmap toward 2030 to achieve 46% carbon emission reduction against 2013.
- One of primal action plans for the 2030 carbon reduction is promoting renewable energy installation, looking at 22~23% of total power consumptions (864TWh) in 2030.
- Japanese government actively promote subsidies for on-site solar and off-site solar physical PPAs.
Implementation:
- Japanese solar market size became around 3.9GWp in 2022. Overall solar will grow at 5.4% per year on average over the next 10 years, with distributed solar accounting for about 90% of the growth from 2021 to 2050
- Current power price hike allows a power user to realize cutting cost and carbon simultaneously even without subsidies.
